By 2030, businesses are expected to spend over $6.6 billion annually on translation services, fueled by the surge in global content. But how can any organisation keep pace with this demand without breaking its budget? This is where machine translation comes in!
Once a far-fetched concept from the Cold War era, this powerful AI technology has quietly evolved from a niche experiment into the engine of our global digital world, now powering global e-commerce, real-time customer support, and international collaboration.
But how does it actually work, and how did it get so good? This article peels back the curtain, exploring What Is Machine Translation, its journey from rigid, rule-based systems to sophisticated neural networks. Read on to discover how this technology is breaking down language barriers and reshaping our digital world.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is Machine Translation?
Machine translation (MT) is one of the types of translation methods that involves the process of using artificial intelligence to automatically translate text from a source language to a different target language without human intervention.
This technology relies on algorithms and machine learning models to
1. Analyse the text
2. Understand its meaning
3. Generate a translation in the desired language.
To help you better understand, below is a quick comparison between computer-assisted machine translation software and professional human translators.
Computer-assisted Translation vs. Human Translation
| Feature | Computer-Assisted Translation (CAT) | Human Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Human-led, enhanced by software tools. | Entirely human-driven. |
| Role of Technology | Software assists with consistency and speed. | Used for research and writing (e.g., dictionaries). |
| Speed | Faster, especially on repetitive content. | Slower and more deliberative. |
| Consistency | Very high due to translation memory tools. | Dependent on the individual translator. |
| Nuance & Creativity | High, as the human has the final say. | Very high; excels at capturing style and tone. |
| Best For | Technical documents, large-scale projects. | Marketing copy, literature, and creative content. |
What Is the History of Machine Translation?

The history of machine translation (MT) mirrors the evolution of computer science, evolving from ambitious ideas to today’s neural network systems.
Phase 1: Early Concepts and Pioneers
In the 17th century, philosophers like René Descartes envisioned a universal language using shared symbols for equivalent ideas. Based on this theory, the first tangible proposals for “translating machines” appeared in the mid-20th century.
In 1933, Soviet scientist Peter Troyanskii created a word-selection machine, and Georges Artsrouni patented an automatic bilingual dictionary that used punched tape.
Phase 2: Georgetown-IBM Experiment
The modern era of machine translation began in 1949 with a memorandum from Warren Weaver, a researcher at the Rockefeller Foundation. Drawing inspiration from World War II code-breaking, Weaver suggested that translation could be viewed as a form of cryptography.
Weaver’s ideas catalysed research that led to the first major milestone in MT history: the Georgetown-IBM experiment in 1954.
This demonstration, a joint effort between Georgetown University and IBM, successfully translated over 60 Russian sentences into English with an IBM 701 computer.
Despite limited vocabulary and grammar, it sparked public and government interest, fueling rule-based MT systems (RBMT) that relied on handcrafted linguistic rules and bilingual dictionaries.
Phase 3: ALPAC Report and AI Winter
Despite early optimism, progress lagged. By the mid-1960s, high-quality translation remained out of reach. The 1966 ALPAC report found MT to be slower, less accurate, and more expensive than human translation, leading to major funding cuts and an “AI winter” for MT research.
Phase 4: The Arrival of Google Translate
Interest again revived in the late 1980s–1990s with Statistical Machine Translation Systems. Pioneered by IBM, SMT used large bilingual corpora to compute translation probabilities. Phrase-based models improved fluency and quality, powering early Google Translate.
Phase 5: The Modern Era’s Large Language Models
The most recent and transformative chapter in the history of machine translation began in the 2010s with the rise of Neural Machine Translation Models.
In 2016, Google announced that it was transitioning its translation service to an NMT system, which marked a significant leap in translation quality.
Today, Large Language Models (LLMs) extend these advances, offering fluent, contextually aware translation outputs and setting new MT standards.
How Does Machine Translation Work?
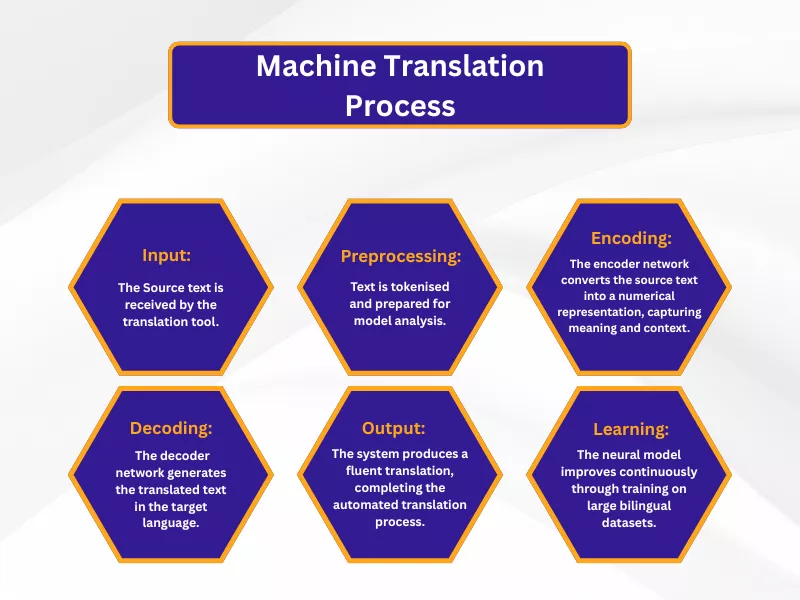
At its core, the translation process of a machine translation engine uses computer software to convert text from one language to another without human involvement.
The primary goal of this technology is to take a piece of text in a different language and make it understandable. There are several ways machine translations accomplish this, but the most advanced and widely used method today involves deep learning.
The general workflow starts with the translation tool receiving the source text. This text is then processed by a neural network that has been trained on vast amounts of data in both the source and target languages. This training allows the system to recognise patterns, grammar, and context, going beyond simple word-for-word substitution.
Modern machine translation uses a sequence-to-sequence model:
1. An encoder network first reads and processes the source text into a mathematical representation that captures its meaning.
2. Then, a decoder network takes this representation and generates the translated text in the target language.
The overall translation workflow is a sophisticated, automated process that can deliver high-quality translations almost instantly.
Types of Machine Translation Technology

There are four main types of machine translation. Each type has a distinct approach to converting text from a source language into a target language.
Rule-Based Machine Translation (RBMT)
Rules-based machine translation is the earliest approach to automatic translation. This method relies on a vast set of hand-crafted linguistic rules and bilingual dictionaries.
Linguists and programmers create complex grammatical, syntactic, and semantic rules for both the source and target languages. The system then uses these rules to analyse the source text and generate a translation.
RBMT can be quite accurate for specific language pairs and domains where rules have been extensively developed. However, it struggles with slang, nuance, and linguistic exceptions not covered by its rulebook.
Statistical Machine Translation (SMT)
Instead of relying on linguistic rules, the Statistical machine translation approach uses machine learning algorithms to analyse massive volumes of existing human translations, known as a bilingual text dataset.
The system learns statistical probabilities of how words and phrases are likely to be translated from one language to another. SMT systems produce more natural-sounding translations than RBMT.
However, SMT can sometimes generate grammatically incorrect or nonsensical sentences if the statistical patterns are weak.
Neural Machine Translation (NMT)
Neural machine translation represents the cutting edge of translation technology and is the model used by most modern translation software.
This approach uses deep learning models, specifically complex neural networks, to model the entire translation process. An NMT system reads a whole sentence at a time, captures the context and meaning, and then generates a translation.
This allows NMT to produce significantly more fluent, accurate, and contextually aware translations than previous methods. This is ideal for effectively handling the complexities and nuances of language.
Hybrid Machine Translation (HMT)
This machine translation approach seeks to leverage the strengths of multiple models by combining them.
For instance, a Hybrid Machine Translation system might use a rule-based engine to pre-process text for a neural network or use statistical models to fill in gaps where NMT might be uncertain.
By integrating different translation methods, HMT aims to produce a higher quality output than any single system could achieve alone. Professional translation services often use this to customise the workflow to achieve the best possible result.
What Are the Benefits of Machine Translation?
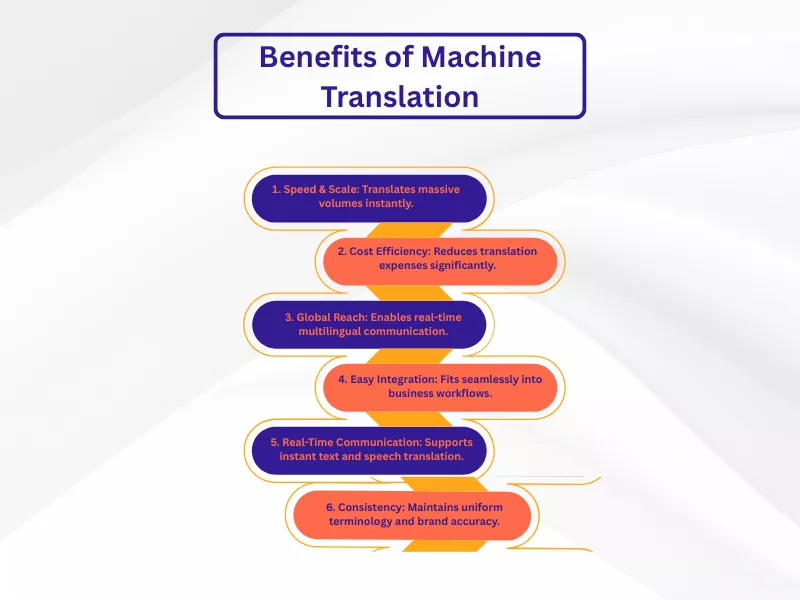
Explore how machine translation benefits today’s language needs:
Exceptional Speed and Scale:
The primary benefit is the ability to translate large volumes of content almost instantly. A robust system can process millions of words in a fraction of the time it would take a human translator, making it ideal for large-scale projects.
Significant Cost Savings:
With less human involvement required for the initial draft, the overall cost of translation is dramatically reduced. This makes it affordable to process large amounts of user-generated content or internal documents.
Instant Global Reach:
A machine translation solution empowers businesses to communicate effectively across languages, breaking down barriers and allowing them to engage with a global audience in near real-time.
Streamlined Workflow Integration:
Machine translation is easily integrated into existing business tools. Modern translation management systems use it to automate the initial translation step, accelerating project timelines.
Enabling Real-Time Communication:
For live interactions such as customer support chats or internal team meetings, machine translation can help facilitate clear communication through instant text translation and speech translation.
Improved Consistency:
Machine translation ensures that specific terminology, brand names, and key phrases are translated consistently across all documents, which is crucial for maintaining brand identity and technical accuracy.
If you are looking for professional machine translation services, OZTranslation Services is one of the trusted language service providers. Get in touch with us to discuss the needs!
What Are Some Use Cases of Machine Translation?
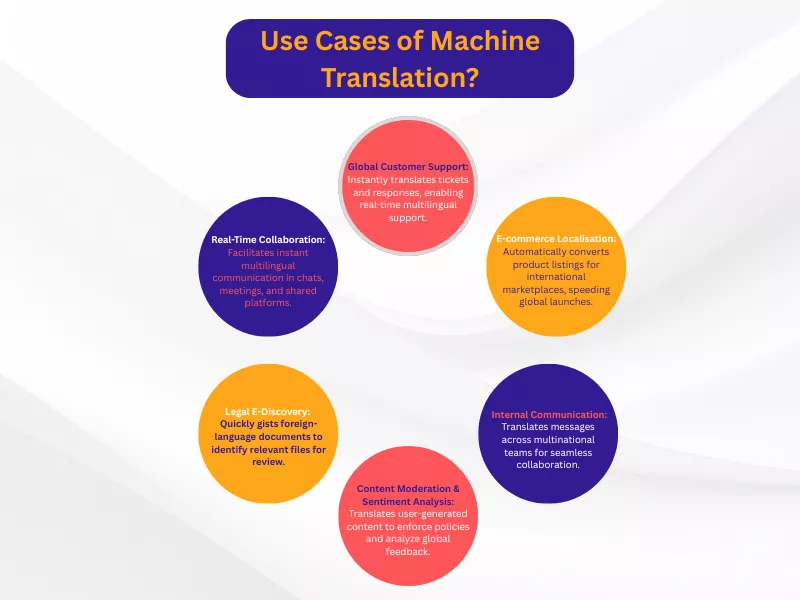
Here are the top use cases of machine translation in today’s world:
Global Customer Support Automation
A customer in Japan can submit a support ticket in Japanese to a U.S.-based company. This ticket is instantly translated into English for the support agent, whose English response is then translated back into Japanese for the customer. This allows a small, centralised support team to handle global inquiries in real-time without hiring agents for every language.
E-commerce Product Listing Localisation
An online marketplace like Amazon or Shopify can use machine translation to automatically populate product descriptions, titles, and specifications across dozens of international storefronts. A seller can upload a product listing in English, and the platform’s language translation engine generates listings for its German, French, and Spanish sites, massively accelerating global product launches.
Internal Communication and Knowledge Sharing
A multinational corporation with offices in Brazil, Germany, and the United States uses machine language translation integrated into its internal chat platform (like Slack or Microsoft Teams). This allows a German engineering team to seamlessly collaborate with their Brazilian counterparts, as messages are translated instantly, preserving the flow of conversation and ensuring no one is left out of critical discussions.
Content Moderation and Sentiment Analysis
A social media platform automatically translates user-generated content, such as comments, posts, and reviews, from around the world. This allows a central moderation team to identify and remove content that violates community standards (like hate speech or spam) regardless of the original language. It also enables the analysis of many translation data points to gauge global user sentiment on new features.
E-Discovery for Legal Cases
During international litigation, a law firm is tasked with reviewing hundreds of thousands of documents in a foreign language. Instead of manually translating everything at enormous cost, they use MT to quickly “gist” the documents and identify which ones are relevant to the case. Only the critical files are then sent to human translators for certified translation, offering a cost-effective choice among various translation options and machine translation methods.
The Challenges and Limitations of Machine Translation
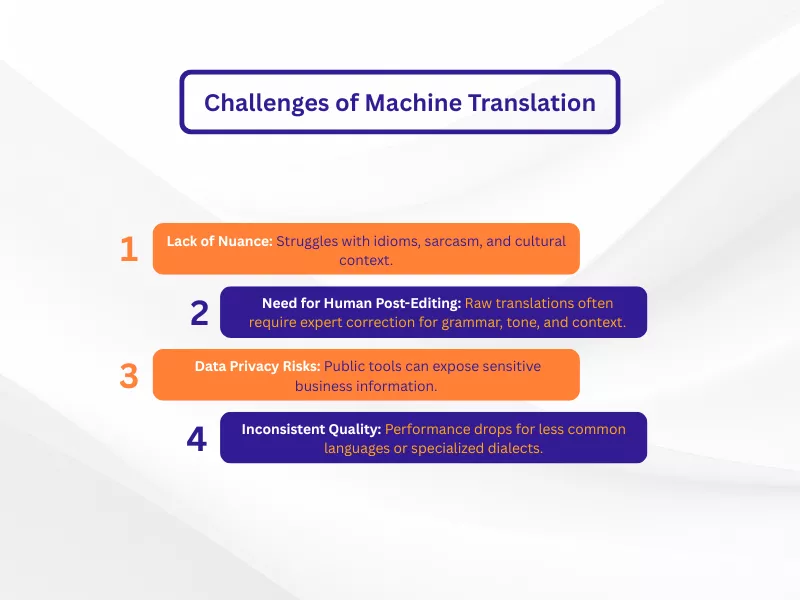
While the benefits are significant, it’s important to understand that machine translation is not a perfect solution. Machine translation has come a long way in terms of speed and basic comprehension, but it still struggles with the complex syntax found in legal and scientific texts. Because the stakes of a filing error are so high, relying solely on AI for a patent translation is generally considered risky. Professional human post-editing is necessary to ensure that the nuanced legal language and precise technical diagrams are communicated with 100% accuracy.
Lack of Nuance and Cultural Context
MT often struggles to capture idioms, sarcasm, and cultural subtleties. A phrase translated literally can lose its intended meaning or, worse, become unintentionally awkward or offensive—a major risk for marketing and brand communication.
The Essential Role of Human Post-Editing
Raw machine translation output is rarely publication-ready. It can contain subtle errors in grammar, tone, or context that only a human expert can identify and correct, making professional post-editing a vital step for high-stakes content.
Data Privacy and Confidentiality Risks
Using free, public online translation tools for sensitive business documents can pose a significant security risk. Confidential information regarding legal, financial, or proprietary matters could be exposed.
Inconsistent Quality Across Languages
MT performance is highest for common language pairs (like English-Spanish) that have vast amounts of training data. For less common languages or specialised dialects, the output quality can be significantly less reliable and more prone to errors.
Looking for Machine Translation Providers? OZTranslationServices Is Here to Help!
At OZTranslationServices, we specialise in human-assisted machine translation services, perfectly designed for multi-scale projects. Our approach combines sophisticated machine translation tools for rapid processing with the critical oversight of professional human linguists who perform meticulous post-editing. This guarantees the ultimate precision your content deserves.
Our services are customised to a specific client’s needs, enabling us to support a variety of industries across 150+ global languages. By integrating seamlessly with your content management systems, we help you accelerate your time to market and connect with a global audience faster and more effectively. Choose OZTranslationServices for a translation solution that delivers both state-of-the-art technology and expert human oversight.
Conclusion: The Future is Hybrid
Machine translation has evolved from theory to an essential force in global communication, enabling rapid, large-scale content translation. Yet technology alone can’t capture cultural nuance or creative intent. The future lies in a hybrid approach, blending advanced algorithms with expert human linguists to achieve the ideal balance of speed, scale, and accuracy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is machine translation in NLP techniques?
Can machine translation replace human translation?
Who is the father of machine translation?
Is ChatGPT a machine translation?
What is the best AI for machine translation?
Which translation tool uses machine learning?
Today, virtually all modern translation tools use machine learning, specifically neural networks. Beyond the major web platforms, this technology is embedded in many places:
1. Professional Translation Software (CAT Tools): Tools like Trados Studio and Phrase (formerly Memsource) integrate with machine learning engines to provide professional translators with instant suggestions.
2. Business Communication Platforms: Apps like Slack and Microsoft Teams have add-ons that use machine learning to translate conversations in real-time.
3. Web Browsers: Browsers such as Google Chrome and Apple’s Safari have built-in translation features that use their own machine learning models to generate a translated web page.
4. Mobile Apps: Mobile-specific apps like iTranslate or SayHi use machine learning to translate spoken conversations, text, and even text from images.
Each of these tools uses a machine learning model to analyse the source text and construct a proper sentence in the target language.
- Tagalog vs Filipino 2026: What’s the Difference? - January 14, 2026
- 8 Tips to Consider Before Hiring a Translation Agency [Best Translation Companies] - December 27, 2025
- Translation vs Transcreation: Which One to Choose? - December 19, 2025